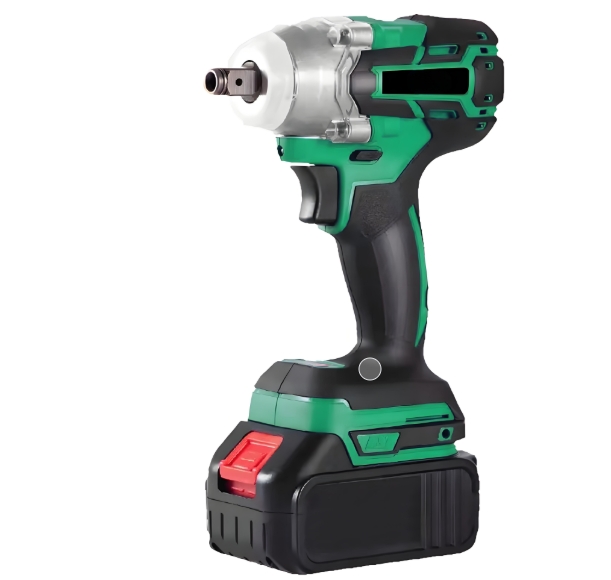
An electric screwdriver is a versatile and indispensable tool used in various industries, from manufacturing and construction to electronics repair. At the heart of this tool lies the electric motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the screwdriver bit. Understanding how the electric motor in an electric screwdriver works is crucial for appreciating the functionality and capabilities of this powerful tool.
The electric motor in an electric screwdriver is a complex piece of machinery composed of several key components, each playing a vital role in its operation.
1. Stator
The stator is the stationary part of the electric motor. It consists of a set of coils, also known as windings, which are typically made of copper wire. These coils are wound around a ferromagnetic core, usually made of iron or steel. The purpose of the stator is to create a magnetic field when an electric current passes through the windings. The magnetic field generated by the stator interacts with the magnetic field of the rotor to produce rotational motion.
2. Rotor
The rotor is the rotating part of the electric motor. It is mounted on a shaft and contains a series of permanent magnets or electromagnets. In the case of a permanent magnet motor, the rotor is equipped with strong permanent magnets that create a magnetic field. In an electromagnet – based rotor, the magnetic field is generated by passing an electric current through coils wound on the rotor. The interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and the rotor causes the rotor to spin.
3. Commutator
The commutator is a crucial component in brushed electric motors, which are commonly used in electric screwdrivers. It is a cylindrical device made of segments of copper or other conductive material, separated by insulating material. The commutator’s role is to reverse the direction of the current in the rotor windings at regular intervals. This is necessary to ensure that the magnetic field of the rotor continuously interacts with the magnetic field of the stator, causing the rotor to rotate in a single direction.
4. Brushes
Brushes are another key component of brushed electric motors. They are made of carbon or a carbon – graphite composite and are in contact with the commutator. The brushes supply electric current to the rotor windings through the commutator. As the rotor rotates, the brushes slide over the commutator segments, ensuring a continuous flow of current to the rotor. However, brushes are subject to wear and tear over time, which can limit the lifespan of the motor and may require periodic replacement.
5. Gearbox
The gearbox is an essential part of an electric screwdriver that connects the electric motor to the screwdriver bit. Its main function is to increase the torque (rotational force) of the motor while reducing the rotational speed. This is achieved through a series of gears with different tooth counts. The gearbox allows the electric screwdriver to generate enough torque to drive screws into various materials, from soft wood to hard metals, while maintaining a manageable rotational speed for precise operation.

The operation of an electric screwdriver motor is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday. When an electric current passes through a conductor (such as the coils in the stator), a magnetic field is generated around the conductor. Similarly, a magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor when there is relative motion between the magnetic field and the conductor.
In an electric screwdriver motor, when the power switch is turned on, an electric current from the power source (usually a battery or an AC adapter) flows through the windings of the stator. This creates a magnetic field around the stator coils. If the motor is a brushed motor, the current also passes through the brushes and the commutator to the rotor windings.
In the case of a permanent magnet rotor, the magnetic field of the stator interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnets on the rotor. According to the laws of magnetism, like poles repel each other, and opposite poles attract each other. As the stator’s magnetic field changes (due to the alternating current in the case of an AC – powered motor or the commutator – controlled current in a DC – brushed motor), it causes the rotor to rotate.
In an electromagnet – based rotor, the current passing through the rotor windings creates a magnetic field in the rotor. The interaction between the stator’s magnetic field and the rotor’s magnetic field results in a torque that causes the rotor to spin. The commutator in a brushed motor ensures that the direction of the current in the rotor windings is reversed at the appropriate times, so that the magnetic field of the rotor continuously interacts with the stator’s magnetic field, maintaining the rotation of the rotor.
The rotational motion of the rotor is then transferred to the gearbox. The gearbox reduces the speed of the rotor while increasing the torque. The output of the gearbox is connected to the screwdriver bit, which rotates to drive screws into or out of materials.
There are several types of electric motors commonly used in electric screwdrivers, each with its own advantages and characteristics.
1. Brushed DC Motors
Brushed DC motors are one of the most widely used types of motors in electric screwdrivers, especially in entry – level and mid – range models. They are relatively simple in design and cost – effective to produce. As mentioned earlier, they consist of a stator, a rotor with windings, a commutator, and brushes. The main advantage of brushed DC motors is their high starting torque, which allows them to quickly overcome the resistance when driving screws into materials. However, they have some drawbacks. The brushes wear out over time, which can lead to reduced performance and the need for replacement. Additionally, the commutator can generate sparks, which may be a safety concern in some environments, such as those with flammable gases or dust.
2. Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors are becoming increasingly popular in high – end electric screwdrivers. They eliminate the need for brushes and the commutator, which significantly reduces maintenance requirements and increases the lifespan of the motor. Instead of using brushes to transfer current to the rotor, brushless DC motors use an electronic controller to switch the current in the stator windings. This results in smoother operation, higher efficiency, and better heat dissipation. Brushless DC motors also offer more precise control over speed and torque, making them ideal for applications that require high – precision screwdriving, such as electronics assembly. However, they are generally more expensive than brushed DC motors due to the complexity of the electronic control system.
3. AC Motors
Although less common in battery – powered electric screwdrivers, AC motors are sometimes used in corded electric screwdrivers. AC motors operate on alternating current, which is typically supplied from a wall outlet. They are known for their reliability and durability. AC motors can generate high torque and are suitable for heavy – duty applications. However, they require additional components, such as a transformer and a rectifier, to convert the AC power to DC power for the motor’s operation in some cases. This can add to the complexity and cost of the electric screwdriver.
1. Bosch
Bosch PS31 – 2A: This is a popular cordless electric screwdriver from Bosch. It features a 12 – volt lithium – ion battery that provides long – lasting power. The motor is a brushless DC motor, which offers high efficiency, low maintenance, and precise control over speed and torque. The PS31 – 2A has two – speed settings, allowing users to choose between a high – speed setting for fast driving and a low – speed, high – torque setting for more demanding tasks. It also comes with a built – in LED light to illuminate the work area, making it convenient for working in dark or confined spaces.
Bosch GSR 18V – 55 Professional: This 18 – volt cordless screwdriver is designed for professional use. It is equipped with a powerful brushless motor that delivers up to 55 Nm of torque, making it suitable for driving large screws into tough materials. The GSR 18V – 55 has a compact and ergonomic design, reducing user fatigue during extended use. It also features a 1 – handed bit change system, allowing for quick and easy bit replacement. The screwdriver comes with two 18 – volt lithium – ion batteries, providing ample power for continuous operation.
2. DeWalt
DeWalt DCF680N: The DCF680N is a 10.8 – volt cordless electric screwdriver from DeWalt. It uses a brushed DC motor and has a compact and lightweight design, making it easy to handle in tight spaces. The screwdriver offers two – speed settings and a maximum torque of 14 Nm. It comes with a belt hook for convenient storage and a built – in LED light. The DCF680N is powered by a lithium – ion battery that offers fast charging times and long – term durability.
DeWalt DCD791D2: This 20 – volt max cordless drill/driver is also a popular choice among professionals. It features a high – performance brushless motor that provides increased runtime and durability. The DCD791D2 has three – speed settings and can deliver up to 534 unit watts out (UWO), which is a measure of the tool’s power. It comes with two 20 – volt max lithium – ion batteries, a charger, and a tough – system storage case.
3. Makita
Makita TD110D: The TD110D is an 18 – volt cordless impact driver from Makita. While it is not a traditional electric screwdriver, it is often used for similar tasks and has a powerful motor. It uses a brushless motor that offers high efficiency and long – tool life. The TD110D has a variable – speed trigger and two – speed settings, allowing for precise control over the driving speed. It can deliver up to 146 Nm of torque, making it suitable for heavy – duty applications. The impact driver also features an LED job light and a built – in holder for an extra bit.
Makita XFD10R: This 18 – volt LXT lithium – ion cordless driver – drill is another popular product from Makita. It has a compact and ergonomic design with a brushless motor that provides up to 50 Nm of torque. The XFD10R offers two – speed settings and a built – in 2 – stage clutch for precise torque control. It comes with a 18 – volt LXT lithium – ion battery and a rapid optimum charger.
4. Milwaukee
Milwaukee M12 Fuel: The M12 Fuel line includes several cordless electric screwdriver models. These tools feature Milwaukee’s patented brushless motor technology, which provides up to 50% more power and 20% more runtime compared to brushed motors. The M12 Fuel screwdrivers have a compact design, making them ideal for working in tight spaces. They offer multiple speed settings and can deliver high torque for various applications. The M12 Fuel line also benefits from Milwaukee’s REDLITHIUM battery technology, which provides longer runtimes and faster charging times.
Milwaukee M18 Fuel: The M18 Fuel series is designed for more heavy – duty applications. The electric screwdrivers in this series are powered by 18 – volt batteries and feature high – performance brushless motors. They can generate up to 115 Nm of torque, making them suitable for driving large screws and bolts. The M18 Fuel screwdrivers have advanced features such as electronic clutch control for precise torque delivery and a high – visibility LED light for working in dark environments.
1. Power Source
The power source of an electric screwdriver has a significant impact on the performance of the motor. In the case of cordless electric screwdrivers, the type and capacity of the battery play a crucial role. Lithium – ion batteries are the most commonly used in modern cordless tools due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and low self – discharge rate. A higher – capacity battery can provide longer runtime, allowing the user to work for extended periods without having to recharge. Corded electric screwdrivers, on the other hand, have a continuous power supply from the wall outlet, which generally allows for more consistent performance but restricts mobility.
2. Motor Design and Type
As discussed earlier, the type of motor (brushed DC, brushless DC, or AC) affects the performance of the electric screwdriver. Brushless DC motors generally offer higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and better control over speed and torque compared to brushed DC motors. The design of the motor, including the number of windings, the strength of the magnets, and the size of the rotor and stator, also influences its performance. A well – designed motor can generate more torque and operate more smoothly.
3. Gearbox Ratio
The gearbox ratio determines how much the speed of the motor is reduced and how much the torque is increased. A higher gearbox ratio will result in lower rotational speed but higher torque. Different applications require different gearbox ratios. For example, driving small screws into soft materials may require a lower torque and a higher speed, while driving large screws into hard materials requires a high torque and a lower speed. The quality of the gears in the gearbox also affects the performance, as worn – out or poorly – made gears can cause inefficiencies and reduced torque transfer.
4. Temperature
The operating temperature of the electric motor can affect its performance. As the motor runs, it generates heat due to the electrical resistance in the windings and the friction in the moving parts. Excessive heat can cause the motor to overheat, which can lead to a decrease in efficiency, reduced torque output, and even damage to the motor. Most electric screwdrivers are designed with cooling mechanisms, such as vents or heat sinks, to dissipate heat and keep the motor within an acceptable operating temperature range.
1. Cleaning
Regular cleaning of the electric screwdriver is essential to keep the motor in good working condition. Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove dust, debris, and metal shavings from the tool’s exterior and ventilation openings. Avoid using solvents or harsh chemicals, as they can damage the plastic and rubber components of the screwdriver. For cordless screwdrivers, also clean the battery contacts to ensure a good electrical connection.
2. Lubrication
The moving parts of the electric screwdriver, such as the gears in the gearbox and the bearings in the motor, need to be lubricated regularly. Use a suitable lubricant recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, prevents wear and tear, and helps to keep the motor running smoothly. However, be careful not to over – lubricate, as excess lubricant can attract dust and debris, causing more problems.
3. Battery Care
For cordless electric screwdrivers, proper battery care is crucial. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and discharging the battery. Avoid overcharging or completely draining the battery, as this can reduce its lifespan. If the battery is not going to be used for an extended period, store it in a cool, dry place at a partial charge. Some modern lithium – ion batteries have built – in battery management systems that help to protect the battery from overcharging and overheating, but proper care is still necessary.
4. Inspection
Regularly inspect the electric screwdriver for any signs of damage, such as cracks in the housing, loose connections, or worn – out brushes (in the case of brushed motors). Check the performance of the motor by testing it on a sample piece of material. If you notice any unusual noises, vibrations, or a decrease in performance, stop using the tool immediately and have it inspected by a professional.
In conclusion, the electric motor in an electric screwdriver is a sophisticated component that plays a central role in the tool’s functionality. Understanding its components, working principle, types, and the factors affecting its performance is essential for choosing the right electric screwdriver for different applications and for maintaining the tool to ensure its long – term reliability. With a wide range of brands and models available, each offering unique features and capabilities, users can select an electric screwdriver that best suits their needs, whether for professional use or DIY projects.
If you want to know more about specific aspects like the latest technological advancements in electric screwdriver motors or comparisons between different models in more detail, feel free to let me know.