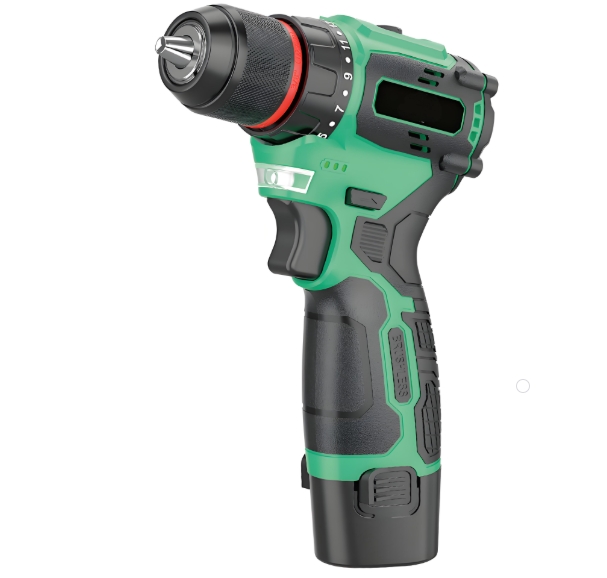
To comprehensively understand what goes into making an electric screwdriver, we need to explore its key components, their functions, and how they work together. An electric screwdriver is a versatile power tool widely used in various industries and households for driving screws efficiently. Here are the essential elements that constitute an electric screwdriver, along with an introduction to some popular brands and models.
The electric motor is the heart of an electric screwdriver, providing the rotational force required to drive screws. There are different types of motors used in electric screwdrivers, each with its own characteristics and advantages.
Brushed Motors: These are the traditional type of electric motors commonly found in many entry – level and mid – range electric screwdrivers. Brushed motors work by using carbon brushes to transfer electrical current to the rotor, which creates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s magnetic field, resulting in rotation. They are relatively inexpensive to produce, making electric screwdrivers with brushed motors more affordable for consumers. For example, the Black & Decker BDCS20C is a popular model that features a brushed motor. It offers a decent amount of torque, making it suitable for a variety of household and light – duty DIY tasks. However, brushed motors have some drawbacks. The carbon brushes wear out over time, which requires periodic replacement. This can lead to increased maintenance costs and downtime. Additionally, they tend to generate more heat and noise compared to other types of motors.
Brushless Motors: In recent years, brushless motors have gained significant popularity in high – end electric screwdrivers. Instead of using carbon brushes, brushless motors use electronic controllers to switch the current in the motor windings, enabling smooth and efficient operation. The Milwaukee M18 Fuel Surge is a prime example of an electric screwdriver equipped with a brushless motor. The brushless design eliminates the need for brush replacement, reducing maintenance requirements. These motors also offer higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and produce less heat and noise. They can deliver more consistent torque, making them ideal for heavy – duty professional applications, such as automotive repair and construction projects.
The gearbox is responsible for reducing the high – speed rotation of the electric motor to a lower speed while increasing the torque. It plays a crucial role in matching the motor’s output to the requirements of driving screws.
Most electric screwdrivers use a planetary gearbox. A planetary gearbox consists of a central sun gear, multiple planet gears that orbit around the sun gear, and an outer ring gear. This design allows for a compact and efficient reduction of speed and multiplication of torque. For instance, the Bosch PS31 – 2A 12 – Volt Max Cordless Screwdriver features a high – performance planetary gearbox. This gearbox design ensures that the screwdriver can handle tough screwing tasks with ease, whether it’s driving large – diameter screws into hard materials or removing stubborn fasteners. The gear ratio of the gearbox can vary depending on the specific design and intended use of the electric screwdriver. A higher gear ratio will result in more torque but lower speed, while a lower gear ratio will provide higher speed but less torque.
The chuck is the part of the electric screwdriver that holds the screwdriver bit in place. There are mainly two types of chucks: keyed chucks and keyless chucks.
Keyed Chucks: Keyed chucks require a separate key to tighten and loosen the jaws that grip the screwdriver bit. They are known for providing a more secure hold on the bit, especially when dealing with high – torque applications. However, they are less convenient to use as the user needs to carry the key around and use it to make adjustments. Keyed chucks are more commonly found in industrial – grade electric screwdrivers where maximum bit security is essential.
Keyless Chucks: Keyless chucks are by far the most popular type in consumer – level electric screwdrivers. They allow users to quickly and easily insert and remove screwdriver bits by simply twisting the chuck. For example, the DeWalt DCF680N 18V Li – Ion Cordless Screwdriver features a 1/4 – inch keyless chuck. This type of chuck offers great convenience, enabling users to switch between different bits in seconds. The jaws of keyless chucks are designed to grip the bit firmly, but it’s important to ensure that the bit is fully inserted and tightened properly to prevent slippage during use.
Since most modern electric screwdrivers are cordless, the battery is a vital component that determines the tool’s runtime and portability.
Nickel – Cadmium (Ni – Cd) Batteries: These were some of the earliest rechargeable batteries used in cordless power tools. Ni – Cd batteries have a relatively high power density and can deliver a good amount of current, making them suitable for powering electric screwdrivers. However, they suffer from the “memory effect,” which means that if they are not fully discharged before recharging, their capacity can gradually decrease over time. They also contain cadmium, a toxic heavy metal, which poses environmental challenges during disposal. For example, some older models of Ryobi electric screwdrivers once used Ni – Cd batteries. As technology has advanced, Ni – Cd batteries have become less common in new electric screwdriver models.
Nickel – Metal Hydride (Ni – MH) Batteries: Ni – MH batteries are an improvement over Ni – Cd batteries. They have a higher energy density, which means they can store more energy in the same size and weight. They also do not suffer from the memory effect as severely as Ni – Cd batteries. Many mid – range electric screwdrivers, such as some models from Craftsman, use Ni – MH batteries. However, they still have limitations in terms of self – discharge rate, which means they lose their charge over time even when not in use.
Lithium – Ion (Li – Ion) Batteries: Li – Ion batteries are the current standard for high – performance cordless electric screwdrivers. They offer several advantages over their predecessors. Li – Ion batteries have a high energy density, allowing for longer runtimes in a compact and lightweight package. They have a very low self – discharge rate, which means they can hold their charge for extended periods when not in use. For example, the Makita XFD10R 18V LXT Lithium – Ion Cordless Driver – Drill features a Li – Ion battery. These batteries also do not have a memory effect, providing consistent performance throughout their lifespan. Additionally, Li – Ion batteries can be recharged quickly, reducing downtime between uses.

The electronics and control system in an electric screwdriver manage the power flow from the battery to the motor and provide various functions and safety features.
Variable Speed Trigger: One of the key features controlled by the electronics is the variable speed trigger. This allows the user to control the speed of the electric screwdriver by the amount of pressure applied to the trigger. A light squeeze on the trigger will result in a slow speed, which is useful for delicate tasks or when starting a screw. Applying more pressure will increase the speed for faster driving. The Panasonic EY7418L 18V Lithium – Ion Cordless Screwdriver has a highly responsive variable speed trigger, providing users with precise control over the tool’s operation.
Torque Control: Torque control is another important function. The electronics can adjust the amount of torque the motor delivers, preventing over – tightening of screws, which can damage the material or the screw itself. Some electric screwdrivers offer multiple torque settings. For example, the Ryobi P238 18 – Volt ONE+ Lithium – Ion Cordless Impact Driver has 18+1 clutch settings, allowing users to select the appropriate torque for different applications, from light – duty assembly work to heavy – duty fastening tasks.
Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS is an integral part of the electronics in an electric screwdriver with a rechargeable battery. It monitors the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature to ensure safe and efficient operation. The BMS prevents overcharging, which can damage the battery and pose a fire hazard. It also protects the battery from over – discharging, which can shorten its lifespan. In addition, it may provide information to the user, such as the remaining battery charge, through an indicator on the tool.
The housing of an electric screwdriver serves several purposes. It protects the internal components from dust, debris, and impact. At the same time, the design of the housing also affects the tool’s ergonomics and user comfort.
Most electric screwdriver housings are made of high – impact plastics, which offer a good balance between durability and weight. Some high – end models may incorporate rubber overmolding on the handle for better grip. For example, the Hilti SFD 5 – A 18 – Volt Cordless Screwdriver has a rubberized handle that provides a secure and comfortable grip, even during extended use. The shape of the housing is also carefully designed to fit the human hand. Tools with an ergonomic design reduce user fatigue and improve control. Some electric screwdrivers have a pistol – grip design, which is similar to the shape of a handgun and is very intuitive for many users. Others may have a straight – shaft design, which can be more suitable for certain applications where a more compact profile is required.
Many modern electric screwdrivers come with additional features that enhance their functionality and usability.
LED Work Lights: An LED work light is a common feature. It illuminates the work area, making it easier to see the screw and the surrounding area, especially in dark or poorly lit environments. For example, the Kobalt KXTS 12 – 03 12 – Volt Lithium – Ion Cordless Screwdriver has an integrated LED work light that automatically turns on when the trigger is pulled, providing instant illumination.
Bit Storage: Some electric screwdrivers have built – in bit storage compartments. This is a convenient feature as it allows users to keep a set of commonly used screwdriver bits with the tool at all times. For instance, the Black+Decker BDCRE20C 20V MAX* Cordless Lithium Ion 4 – Position Screwdriver has a bit holder that can store several bits, ensuring that users have the right bit on hand when needed.
Quick – Release Mechanisms: In addition to keyless chucks, some electric screwdrivers may have quick – release mechanisms for other components, such as battery packs. This enables users to quickly swap out batteries, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. The DeWalt DCF880C2 18V Li – Ion Cordless Impact Driver has a simple and efficient battery release mechanism, allowing for seamless battery changes.
In conclusion, an electric screwdriver is a complex piece of equipment composed of multiple key components, each playing a crucial role in its operation. From the powerful electric motor to the ergonomic housing, and the advanced electronics to the reliable battery, all these elements work in harmony to provide users with a convenient and efficient tool for driving screws. The variety of brands and models available in the market offer different combinations of features and performance levels, catering to the diverse needs of consumers, from DIY enthusiasts to professional tradespeople. Whether you are looking for an affordable option for light household tasks or a high – performance tool for heavy – duty industrial applications, there is an electric screwdriver out there with the right components to meet your requirements.